Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
Heat Capacity and Latent Heat: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Specific Heat Capacity, Molar Heat Capacity & Molar Heat Capacity for Different Atomicities etc.
Important Questions on Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
If we place Lithium metal in coffee cup calorimeter that already contains of water. The specific heat capacity of reaction mixture is . Temperature of water is increased from to . Then find for the reaction.
One gram sample of is decomposed in a bomb calorimeter temperature increases by . The heat capacity of the system is . What is the molar heat of decomposition for ?
A diatomic gas is supplied heat with keeping the pressure is constant. The ratio of is
A certain amount of heat supplied to of nitrogen at room temperature to rise its temperature by at constant pressure. The amount of heat required is (Molecular mass of nitrogen is and )
An ideal gas At S.T.P requires 12 calories to produce 4.48 litres and the temperature is raised by . Calculate the Cp of the gas
The ratio of pressure and volume is constant and is equal to for a monoatomic gas, then the molar heat capacity at constant pressure would be-
Find out the molar heat capacity of the gas when a monoatomic ideal gas undergoes a process in which the ratio of to at any instant is become constant and equals to 1 ?
What is R in the following equation?
Among the following statements, select the correct statements.
I. Combustion of organic compounds is an exothermic reaction.
II. There is decrease in entropy by crystallisation of a liquid into a solid.
III. The molar enthalpy of vapourisation of acetone is less than that of water.
At STP, an unknown gas of volume , requires of heat to raise its temperature by at a constant volume. The gas is
Find the specific heat capacity at constant volume for an ideal gas with molecular mass of the gas is M. For an ideal gas .
A monatomic ideal gas undergoes a process in which . What is the molar heat capacity of the gas?
Which of the following expressions is true for one mole of a liquid?
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is mixed with one mole of an ideal diatomic gas. The molar specific heat of the mixture at constant volume is (in Calories)
Give integer as answer.
of ice at is added to 340g of water at . The final temperature of the resultant mixture is . The value of (in g) is closest to
[Heat of fusion of ice ; Specific heat of water ]
Assertion: Specific heat of gas at constant pressure is greater than its specific heat at constant volume.
Reason: At constant pressure, some heat is spent in expansion of the gas.
The value of and for a gas are R and R. The vapour density of gas is . Its atomic mass will be
Equal volumes of monoatomic and diatomic gases are taken at same temperature and pressure. The ratio of adiabatic exponents of the gases will be-
A monoatomic ideal gas goes through a process in which, the ratio of to at any instance is constant and equal to unity. The molar heat capacity of gas is
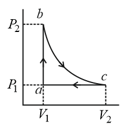
Carbon monoxide is carried around a closed cyclic process , in which is an isothermal process, as shown in the diagram. The gas absorbs of heat as its temperature is increased from to in going from to . The quantity of heat ejected by the gas during the process is